In enzymology, a 4-coumarate—CoA ligase (EC 6.2.1.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- ATP 4-coumarate CoA AMP diphosphate 4-coumaroyl-CoA
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, 4-coumarate, and CoA, whereas its 3 products are AMP, diphosphate, and 4-coumaroyl-CoA.
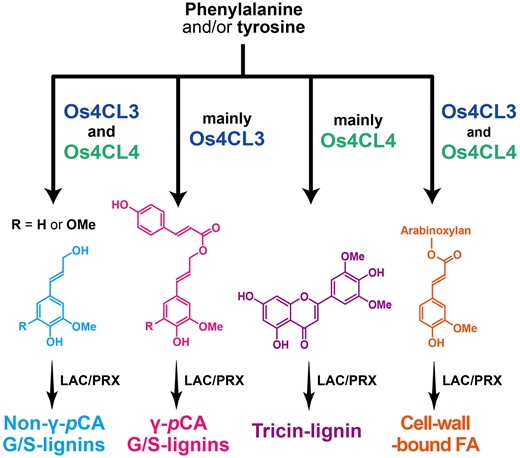
This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, to be specific those forming carbon-sulfur bonds as acid-thiol ligases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include 4-coumaroyl-CoA synthetase, p-coumaroyl CoA ligase, p-coumaryl coenzyme A synthetase, p-coumaryl-CoA synthetase, p-coumaryl-CoA ligase, feruloyl CoA ligase, hydroxycinnamoyl CoA synthetase, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase, caffeoyl coenzyme A synthetase, p-hydroxycinnamoyl coenzyme A synthetase, feruloyl coenzyme A synthetase, sinapoyl coenzyme A synthetase, 4-coumaryl-CoA synthetase, hydroxycinnamate:CoA ligase, p-coumaryl-CoA ligase, p-hydroxycinnamic acid:CoA ligase, and 4CL. This enzyme participates in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis.
References
- Gross GG, Zenk MH (1974). "Isolation and properties of hydroxycinnamate: CoA ligase from lignifying tissue of Forsythia". Eur. J. Biochem. 42 (2): 453–9. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03359.x. PMID 4364250.
- Lindl T, Kreuzaler F, Hahlbrock K (1973). "Synthesis of p-coumaroyl coenzyme a with a partially purified p-coumarate:CoA ligase from cell suspension cultures of soybean (Glycine max)". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 302 (2): 457–64. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(73)90174-5. PMID 4699252.


![[PDF] Cloning and Functional Characterization of Two 4Coumarate CoA](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7343f3400ec4b945c9568310ffc869125053df0f/4-Figure4-1.png)
![[PDF] Characterization and the expression profile of 4coumarate CoA](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/4e8d40eb0029b903b87ea131cb0b59410bc034e4/2-Figure1-1.png)